How to Spend Less Time on Email: 12 Tips for Keeping Your Inbox Under Control
Clarke McEwan Accountants
Managing your email inbox can feel like playing a never-ending game of whack-a-mole. Just when you think you've gotten to inbox zero and start doing your little victory dance ... up pops another email. And another one.
What's worse, the sheer volume of email we get often exceeds the time we can afford to deal with it. This becomes a bigger issue when we let our guilt get the better of us -- the guilt that comes with not responding right away, responding curtly, or not responding at all.
But the fact is, there are more important things on our to-do lists than email. Want to spend less time living in your inbox, and more time doing the stuff that actually matters? Here are 12 tips to get you started.
12 Tips For Better Email Management
1) Unsubscribe. Ruthlessly.
The easiest way to maintain inbox zero? Get less email. The very first step to achieve an emptier inbox is unsubscribing from every single email list that doesn't provide you with value on a regular basis.
In fact, my recommendation is to unsubscribe from everything. Take a few days to let it sink in, and then re-subscribe only to the newsletters you really, truly miss. In this step, you might consider converting any daily digests you used to follow to weekly ones.
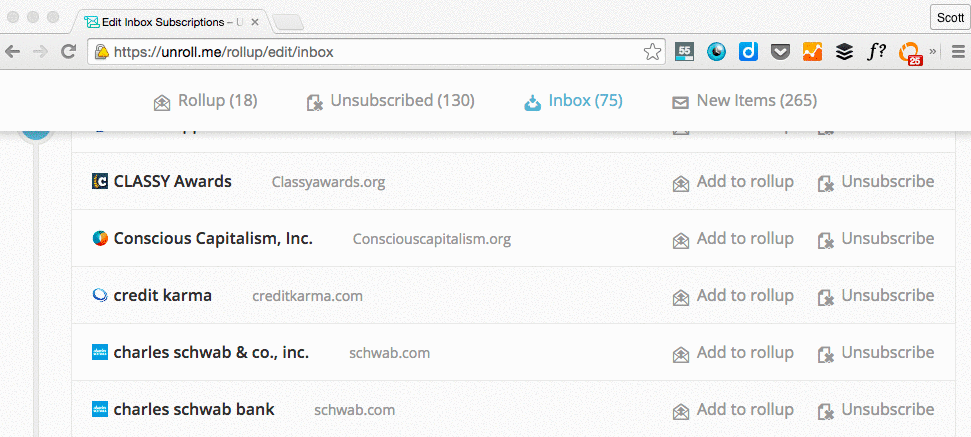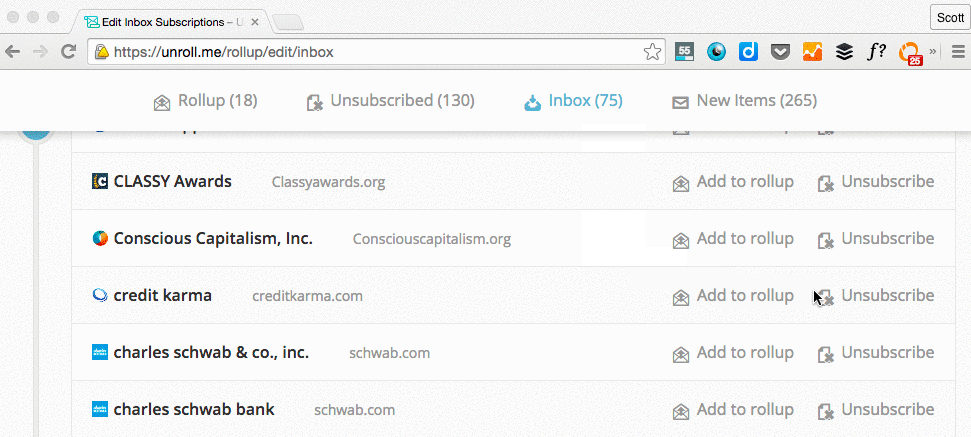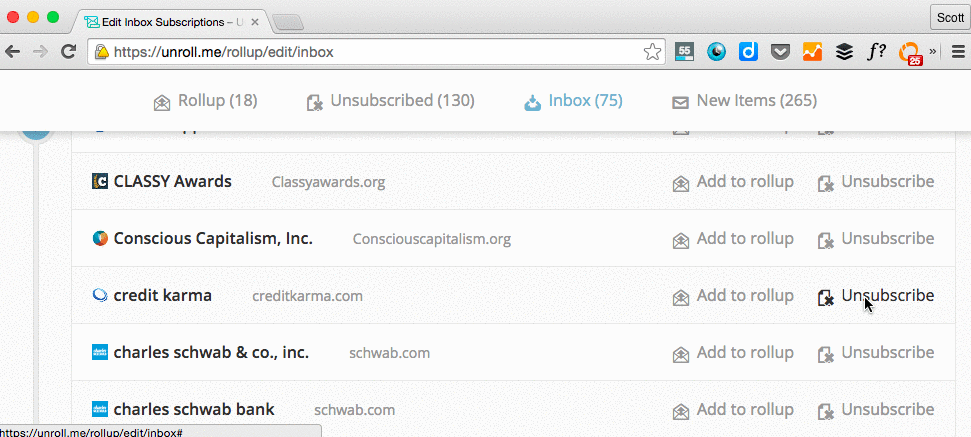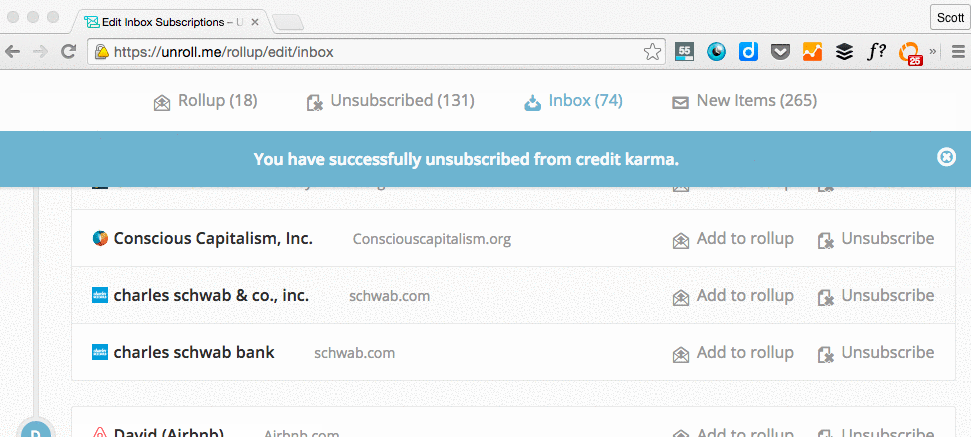
While unsubscribing manually from tens -- hundreds? -- of newsletters one by one sounds tedious, there are tools out there that can help you do it in just a few clicks. Unroll.me is my personal favorite: It's a free tool that lets you mass unsubscribe from all the newsletters you don't read. You can either unsubscribe from everything at once (my recommendation), or you can pick and choose. Read this blog post to learn more about how it works.
2) Remove yourself from any internal company and business threads you don't need to be on.
Once you've unsubscribed from external newsletters, it's time to evaluate the internal emails you receive on a regular basis. Do you really need to get email notifications every time the sales team closes or deal, or every time someone on the marketing team reports a bug?
If the answer isn't a definitive "yes," do yourself a favor and remove yourself from whatever alias or list you're on. If that makes you wildly uncomfortable, compromise by creating a folder in your email client and send those emails to that folder automatically. (To set at up, you can create filters in Gmail or rules in Outlook.)
3) Understand -- and embrace -- that you can't respond to everything.
Part of maintaining a manageable inbox -- and your sanity -- is to change the way you think about email a little bit. Only you can decide what deserves your very limited time and attention. When it comes to email, understand that there's simply no way you'll be able to respond to every single email that arrives in your inbox, let alone read them all.
I love the way Merlin Mann puts it : "Stop thinking of emails like precious family heirlooms, and start treating 'em like pints of milk. Perishable, time-stamped milk that becomes a little less fresh every day until it smells kind of funny and just needs to be dumped. Believe me, there will always be more coming."
So if you're looking at an email and know in your heart of hearts you're never going to respond to it, archive it. Better yet, delete it. As Mann says , "Trust your instincts, listen to them, and stop trying to be perfect."
4) Keep your replies brief whenever possible.
When you do have to reply to an email, you'll find that in most cases, you don't need to craft the perfect response. Often, a few sentences will do; in some cases, a few words. If you let an email with an action item sit for a few days, a quick "Do you still need this?" email might end up saving you a lot of time.
Don't feel guilty about sending succinct emails. If you're concerned your brevity will be taken the wrong way, give a heads-up to the folks you exchange emails with the most. Tell them that, in your effort to spend less time on email and more time on your actual work, you plan to cut down word count in your emails.
The better you get at deleting emails you don't need to read or respond to, the more time you'll have to write the emails that warrant those long responses.
5) Use pre-written replies.
Which types of emails do you find yourself typing out over and over, without really needing to customize them?
I, for example, often find myself referring people to HubSpot's guest blogging guidelines page. I used to write one-off emails to folks, meaning I'd have to craft a few sentences, find and copy the link, and so on. Now, I give myself ten minutes back in my day by sending pre-written replies via Gmail's "canned responses" feature.
Gmail, Outlook, and other email clients offer canned responses. Below are instructions for setting up and using them in Gmail.
To Set Up Canned Responses in Gmail:
- Click the gear icon in the upper right-hand corner and choose "Settings."
- Click the "Labs" tab, find Canned Responses at the top, and click "Enable." Scroll down and click "Save Changes."
To create a canned response, compose a new email and click the little arrow in the bottom right-hand corner of the new email. Choose "Canned responses," and then "New canned response." From there, you can name your new canned response, write it, and save it. Anytime you want to use it, simply go back to that little arrow, choose "Canned responses," and click on the one you'd like to use. (Learn more on Google's website.)
To Set Up Canned Responses in Outlook:
In Outlook, the best option I could find was to set up your canned responses as "Signatures." That way, when you reply to an email, you can choose the appropriate "signature" and the whole canned reply will appear. Here's how to do that:
- On the Outlook menu, click "Preferences." Under "E-mail," click "Signatures."
- Click the plus icon to add a new signature.
- A new signature will appear under "Signature name" with the label "Untitled." Double-click "Untitled," and then type in a new name for your canned response.
- In the right pane, type the text that you want to include in the signature -- in other words, type in your canned response.
Once you create the canned response as a signature, you can add it to a new email by clicking in the message body, choosing the "Message" tab, clicking "Signatures," and choosing a signature from the list. (Learn more on Outlook's support page.)
6) Employ a one-click rule.
This rule might seem simplistic, but it's a huge time-saver. The "one click" refers to a single click to open an email once. Once it's open, decide exactly what you want to do with it right then and there: Reply, forward, send to a folder, archive, and/or delete.
The point here is to not open an email, read it, and then decide to deal with it later and move on. That's the bad habit that'll guarantee you a clogged inbox and more stress down the road.
7) Triage emails using "special stars" in Gmail.
If you use Gmail and your goal is to get to inbox zero and maintain it, then I'd like to direct you to the email system that's changed the way I do email. Here are the full instructions. This works great in conjunction with the one-click rule we just talked about.
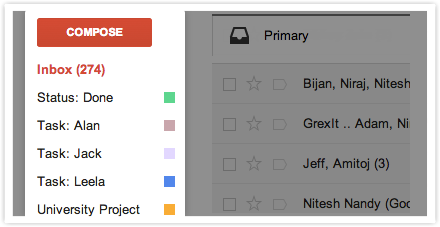
The premise is this: In Gmail, you'll set up multiple inboxes and give each of them a name, like "Needs Action/Reply" and "Awaiting Response." Your general inbox will then appear on the left, and your labeled inboxes (which Gmail calls "panes") will appear on the right, like so:
You'll use what Gmail calls "special stars" -- kind of like Gmail's labels, but better -- to categorize every single email that comes into your inbox.
Every time you get a new email in your inbox, you'll want to:
- Reply to the ones you can right away.
- Label the emails you need to deal with later by marking them with the appropriate special star.
- Archive or delete any emails you don't need to deal with.
In the end, you'll archive everything. Your inbox will stay at zero, and everything else will either be in its designated pane, archived, or deleted.
Use Outlook?
SimplyFile is a free organizational tool that'll help you categorize emails using folders. When an email comes in, all you have to do is drag it into the appropriate folder. You can organize both messages you're receiving in your inbox, as well as messages you're sending -- which you can file as you send them.
Image Credit: SimplyFile
8) Delegate emails to others using a collaboration tool.
Sometimes, you might find that you receive emails that are better handled by someone else. In these cases, you could either forward the email, or you can streamline the process by quickly sharing the email with someone on your team using an email collaboration tool.
There are a number of email collaboration tools out there to choose from. If you use Gmail, Hiver is a great choice: It lets you share Gmail labels (and therefore share folders) with other users, which you can use to assign tasks, delegate emails, and even track their status if you want to. If you need to add a quick note explaining what's going on in an email thread, you can do that right in the tool.
Image Credit: Hiver
9) Use the "yesterbox" approach.
"Yesterbox" is a methodology for managing your inbox created by Zappos CEO Tony Hsieh. This approach is kind of like inbox zero, except you're working off all the emails from yesterday and treating them like today's to-do list.
The basic premise is this: Every morning, you have a fixed number of emails to answer instead of an endless flood of new emails coming in. Once you finish dealing with yesterday's emails, you're done with email for the day. Here are the full instructions .
Like Klinger's methodology from #7, you'll categorize incoming emails into folders labeled "Yesterbox," "Today," "Action Required," "Awaiting Response," and so on. As new emails come in, you'll label them accordingly. But as for actually dealing with these emails -- that's left for a specific time on your calendar that you've designated for handling yesterday's emails. In the end, your Yeseterbox is a to-do list with static tasks.
It's that freeing sense of completion that makes this method so appealing -- but be wary that if your job requires you to tackle emails as they come in, this may not be the best method for you.
10) Set up filters when you go on vacation.
Vacations are awesome, but coming back to a jam-packed inbox is ... not so awesome. One way to manage your email workflow while you're gone for long periods of time is to set up filters.
This is an approach HubSpot's Director of Marketing Rebecca Corliss found worked really well for her when she went on her month-long sabbatical. Corliss was working in Gmail, but you can adapt this method for most email clients. In short, here's what she did:
- She created a new folder for her vacation ("Spain Sabbatical 2015").
- She set up a filter that recognized any emails being sent to *@hubspot.com. By putting the asterisk there instead of her actual email, she was able to capture not only emails that were sent to her work email address, but also emails sent to the company aliases she was on.
- She added a second filter that deleted irrelevant emails -- for example, all the daily and weekly digests she expected to receive, like metrics updates.
- When she returned, she strategically handled all her unread emails. For example, she searched for emails she wanted to respond to first by conducting key searches for her manager's email address.
Once these more time-sensitive messages are addressed, she blocked time to go through the remaining emails and respond only to the ones that were absolutely necessary. Here are the full instructions .
11) Block time to get back to inbox zero.
Dedicating specific chunks of time to get back to inbox zero isn't just for when you return from vacation. It should be something you tackle in short batches on a daily basis, and in larger chunks every week or so, depending how much new email you receive.
The purpose of batching email? So you aren't handling emails as they arrive. That can be a serious productivity killer, and can pull you away from projects and tasks that are more important than a perfectly clean inbox.
On a daily basis, limit yourself to dealing with new emails during fixed periods each day. For example, HubSpot Demand Generation Manager Amanda Sibley physically blocks off an hour in the morning and an hour in the evening on her calendar for getting her inbox in order. Do what works for you.
12) Use keyboard shortcuts.
To make the process of reading, replying to, archiving, and deleting emails a lot faster (and generally more enjoyable), take advantage of any keyboard shortcuts your email client offers. Here are tips for keyboard shortcuts in Gmail and Outlook. If you use a different email client, do a quick Google search for the name of your email client + "keyboard shortcuts."
Keyboard Shortcuts in Gmail:
First thing's first: You'll need to activate keyboard shortcuts. To do this:
- Click the gear icon in the upper right-hand corner and choose "Settings."
- Click the "General" tab, find "Keyboard shortcuts," and select "Keyboard shortcuts on." Scroll down and click "Save Changes."
- Then, go back to "Settings" via that gear icon, click on the "Labs" tab, and find "Custom keyboard shortcuts" (by Alan S). Choose "Enable." Scroll down and click "Save Changes."
Once custom keyboard shortcuts are turned on, a new tab will appear in your Settings called "Keyboard Shortcuts." Head over there to learn the default keyboard shortcuts and customize them if you'd like.
Keyboard Shortcuts in Outlook:
Outlook doesn't let you customize keyboard shortcuts, but they have a heck of a lot to choose from. Here's the full list , and below are some favorites:
- Create a new message: ? + N (Mac); Ctrl + N (PC)
- Send an open message: ? + Return (Mac); Ctrl + Return (PC)
- Save an open message and store it in Drafts: ? + S (Mac); Ctrl + S (PC)
- Forward a message: ? + J (Mac); Ctrl + J (PC)
- Display the next message: Control + ]
- Display the previous message: Control + [
- Delete the selected message: Delete
- Mark selected messages as read: ? + T (Mac); Ctrl + T (PC)
Looking for more ideas for gaining and maintaining control of your email? Here are 11 inbox organization tools to try, as well as four solutions to getting "inbox zero" based on your personality.